KEDRAB® (Rabies Immune Globulin [Human]) Has Been Evaluated in 4 Clinical Studies and Is the Only HRIG With Established Effectiveness in Children1
Click on the tabs below to view details on the primary studies determining the effectiveness of KEDRAB in pediatric and adult subjects.
- Study 004
(Pediatric patients) - Study 003
(Safety/Tolerability) - Study 23630
(PK of rabies antibodies) - Study 24061
(Interference of active antibodies)
A multi-center, open-label post-marketing study measured the safety and efficacy of KEDRAB in 30 pediatric patients (0.5-14.9 years of age) exposed or possibly exposed to rabies virus (patients were indicated for post-exposure prophylaxis and administered KEDRAB concurrently with a full course of active rabies vaccine). Subjects received KEDRAB 20 IU/kg, and as much of the dose as anatomically feasible was infiltrated into and around the wound site when detectable. The remaining amount was injected intramuscularly.1
Efficacy Results
93.3% of Subjects Had Day 14 RVNA Titers ≥0.5 IU/mL1,2 |
|
|---|---|
| Participants free of active rabies infection, no. (%) | |
| At day 14 | 30 (100) |
| At day 84 | 30 (100) |
| RVNA titer | |
| No. of participants with RVNA titer ≥0.5 IU/mL at day 14 | 28 (93.3) |
| Mean ± SD | 18.89 ± 31.61 |
| Median | 8.81 |
| Range (min – max) | 0.21–153.62 |
Percentages are based on the number of participants in the as-treated population. RVNA titers denote the geometric mean of the results per participant per visit.
min – max, minimum to maximum; RVNA, rabies virus neutralizing antibody; SD, standard deviation.
- No subject developed rabies infection through Day 841
HRIG REAL-WORLD EVIDENCE1
Based on claims data, 172 US children (≤17 years) were treated with KEDRAB between 2018-2020.
Based on Centers for Disease Control data, no children in the US treated with post-exposure prophylaxis have been reported to have had rabies between 2018-April 2021. CDC has not reported any rabies deaths in 2022 and 2023.
A phase 2/3, single-center, prospective, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study evaluating the safety and effectiveness of KEDRAB vs HRIG Comparator when coadministered with rabies vaccine (RabAvert®) in 118 adult subjects.1
Study subjects were healthy adults 18 to 72 years of age who were without significant acute or chronic illness. Participants were predominantly white (93%) and 64% were women.1
Study objectives3:
- Evaluate the safety and tolerability of KEDRAB vs HRIG Comparator
- Determine whether KEDRAB interferes with the development of active anti-rabies antibodies when given simultaneously with active rabies vaccine, as compared to HRIG Comparator, also given simultaneously with the active rabies vaccine
Efficacy Results
Subjects With Mean Anti-Rabies Antibody Titer ≥0.5 IU/mL on Day 141* |
||
|---|---|---|
| KEDRAB With Rabies Vaccine (N=57) | HRIG Comparator With Rabies Vaccine (N=59) |
|
| Rabies virus neutralizing antibody titer ≥0.5 IU/mL, n (%) | 56 (98.2) | 59 (100) |
| 95% CI for proportion (%) | (90.6, 100) | (93.9, 100) |
| Difference (KEDRAB – HRIG Comparator) (%) | -1.8 |
|
| 90% CI for difference† (%) | (-8.1, 3.0) |
|
*Adapted from KEDRAB Prescribing Information.1
†Based on Farrington-Manning score statistic.
CI, confidence interval.
- 98.2% of subjects in the KEDRAB group and all subjects in the HRIG Comparator group had an anti-rabies antibody titer by rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test of ≥0.5 IU/mL on day 141
Mean (+SD) Plasma HRIG Concentrations for KEDRAB and HRIG Comparator1*
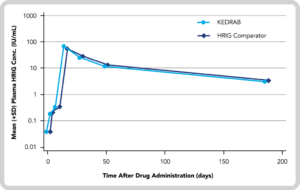
- No statistically significant differences in plasma antibody titer pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters (Cmax, AUC0-last, or AUC0-inf) between treatment groups3
- However, the geometric mean RVNA titer on the Day 3 visit was statistically significantly lower with KEDRAB than with HRIG Comparator (P=0.0003)3
PK Comparison of Rabies Virus Neutralizing Antibody Between KEDRAB and HRIG Comparator Administered With Rabies Vaccine1
Geometric LS Mean Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Units | KEDRAB (Test) | HRIG Comparator (Reference) | Test/Reference (%) | 90% CI (%) |
| Cmax | IU/mL | 44.87 | 36.02 | 124.59 | 90.62-171.28 |
| AUC0-last | Day•IU/mL | 1741.40 | 1686.03 | 103.28 | 79.03-134.98 |
| AUC0-inf | Day•IU/mL | 2045.87 | 1916.90 | 106.73 | 80.48-141.54 |
*Adapted from KEDRAB Prescribing Information.1
AUC, area under the concentration-time curve; CI, confidence interval; Cmax, maximum concentration; inf, infinity.
KEDRAB is non-inferior to HRIG Comparator when administered in combination with a rabies vaccine for post-exposure prophylaxis1
A phase 1, randomized, single-dose, double-blind, 2-period, crossover pharmacokinetic (PK) study compared KEDRAB with HRIG Comparator in 26 subjects between 18 and 45 years of age4
Study objectives4:
- Evaluate the PK of rabies antibodies in subjects receiving KEDRAB (who have not previously received rabies vaccination)
- Monitor any adverse events following administration of a single intramuscular (IM) injection of KEDRAB
- No clinically meaningful conclusions to be made with regard to AEs, laboratory values, or vital signs
PK Results
Median Anti-Rabies Antibody Titer PK Findings for Each Dose Administered4* |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Cmax† (IU/mL) | Tmax (days) | AUCT (days•IU/mL) | AUCI (days•IU/mL) | t1/2 (days) |
| KEDRAB
20 IU/kg | 0.249 (0.063) | 7.0
(3 – 14) | 5.2 (1.3) | 6.7 (1.27) | 17.9 (6.37) |
| HRIG Comparator
20 IU/kg | 0.302 (0.068) | 3.0
(3 – 14) | 6.3 (1.24) | 8.0 (1.36) | 17.8 (6.74) |
*Adapted from Data on file, Kamada Ltd.4
†Represents the average of Cmax and t1/2 obtained during the entire study.
All values in parentheses are mean and standard deviation except Tmax which is median (range).
AUC, area under the concentration-time curve; Cmax, maximum concentration; IM, intramuscular; t1/2, terminal elimination half-life; Tmax, time to maximum concentration.
Mean Plasma Anti-Rabies Antibody Titer vs Time Profile (Log Scale Following Administration of IM KEDRAB 20 IU/kg or IM HRIG Comparator 20 IU/kg)4*
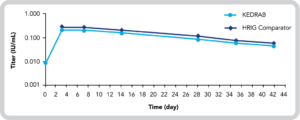
IM, intramuscular
- The point estimate for the ratio of anti-rabies antibody titer AUCI values of KEDRAB and HRIG Comparator was 84.4 (90% CI, 78.6%-90.7%)4
- There was no statistically significant difference (P=0.4491) in anti-rabies antibody titer Tmax values between KEDRAB and HRIG Comparator4
- There was a marginally statistically significant sequence effect seen for Cmax (P=0.042) and AUCT (P=0.033). While the latter point indicates a slight difference between the 2 products, it is apparently due to a treatment-by-period interaction.4
Overall, plasma anti-rabies antibody titers achieved with KEDRAB were comparable with HRIG Comparator4
A phase 1, double-blind, one-period, single-dose pharmacokinetic (PK) study evaluated KEDRAB when administered with 3 doses of rabies vaccine (Rabipur®) in 16 subjects between 18 and 45 years of age4
Study objectives4:
- Assess whether KEDRAB interfered with the development of antibodies when given simultaneously with rabies vaccine (Rabipur®)
- Monitor any adverse events following coadministration of a single IM injection of KEDRAB and repeated injections of an active rabies vaccine
PK Results
Median Anti-Rabies Antibody Titer PK Findings for Each Dose Administered4* |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Cmax (IU/mL) | Tmax (days) | AUCT (days•IU/mL) |
| KEDRAB 20 IU/kg | 9.4 (10.72) | 42 (42-42) | 85.2 (92.2) |
| Saline Placebo | 24.0 (21.1) | 42 (14-42) | 276.3 (204.7) |
*Adapted from Data on file, Kamada Ltd.4
All values in parentheses are mean and standard deviation except Tmax which is median (range).
AUCT, area under the concentration-time curve; Cmax, maximum concentration; Tmax, time to maximum concentration.
- The Cmax for rabies antibodies for KEDRAB plus vaccine appeared to be substantially lower compared to placebo plus vaccine (42.9%)4
- No statistically significant difference could be determined between Cmax from the test and placebo formulation due to a high degree of variability in the data4
Mean Plasma Anti-Rabies Antibody Titer vs Time Profile (Semi-Log Scale) Following Administration of IM KEDRAB 20 IU/kg or Saline With 3 Doses of Rabipur®4*
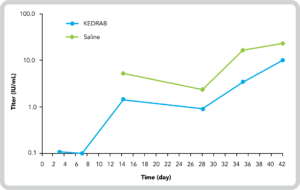
*Adapted from Data on file, Kamada Ltd.4
- The mean AUC1 for KEDRAB plus vaccination was statistically significantly lower compared to placebo plus vaccine4
KEDRAB inhibited rabies antibody production following immunization with a rabies vaccine (Rabipur®)4
All trademarks are property of their respective owners.
References: 1. KEDRAB [package insert]. Fort Lee, NJ: Kedrion Biopharma Inc.; 2021. 2. Hobart-Porter N, Stein M, et al. Safety and efficacy of rabies immunoglobulin in pediatric patients with suspected exposure [published online ahead of print, 2021 Feb 9]. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021;1-7. doi:10.1080/21645515.2020.1854000. 3. Matson MA, Schenker E, Stein M, Zamfirova V, Nguyen H, Bergman GE. Safety and efficacy results of simulated post-exposure prophylaxis with human immune globulin (HRIG; KEDRAB) co-administered with active vaccine in healthy subjects: a comparative phase 2/3 trial. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020;16(2);452-459. doi:10.1080/21645515.2019.1656967. 4. Data on file. Kamada Ltd.

